
Here we explain the simplest way to draw a graph withĬommands to Quit, Read a Command File, and Save Parameters commands to define a function, substitute variables, and calculateĪctually there are more commands which cannot be categorized into the itemsĪbove, so that it is hard to explain everything here.commands to quit, read a command file, and save parameters.Type `help` to access the on-line reference manual.Īt the "gnuplot> " prompt you can use the following commands: Throughout the 4.0 series, but all save files use the new syntax. Please refer to the documentationįor command syntax changes. Thomas Williams, Colin Kelley and many others Gnuplot isĪ command line driven plotting tool. Shows a gnuplot command line prompt "gnuplot> ". Gnuplot displays a banner and credit, then Is common to those systems, so that this tutorial may be helpful forįirst of all, exec gnuplot. Introduction to gnuplot for the case of UNIX, X11.

#Ubuntu gnuplot install#
+ ++ 4.6 angles animation ANOVA arrow axes background basics bessel binary border boxes cairolatex call circle cntrparam colormap configuration contour csv cube dashed data datafile depthorder dgrid3d do documentation epslatex errorbars eval fill filledcurves fit for format functions gif grid head hidden3d histogram HSV if image implicit index install interactive interpolate invert isosamples italic iteration jpg key label labels legend linecolor lines linespoints linestyle linetype list load logscale lua macros margin Matlab matrix maxcolors multiplot non-continuous object palette parametric pm3d png points polygon postscript ratio rect rectangle relative reread rgb rgbimage samples separator size sort special-filenames sphere splot sprintf standalone standard input stats steps string style svg symbols system table terminal tics tif tikz transparent Ubuntu variable vectors wave field word wxt xticlabel zoom Now we can save the file, run the above command again and hopefully get the following figure. Also, we scale the length of the tics, because the default length is a bit too long. For the ytics we tell gnuplot to make a tic every multiple of 1. After that, we specify the positions of the xtics and set strings (note that we can directly use utf-8 strings here) to the given positions. # Axes tics set xtics ( '-2π' -2 * pi, '-π' -pi, 0, 'π' pi, '2π' 2 * pi)Īt first we set the legend to a specific position, put labels on the axes and set the ranges of the axes. # Axes label set xlabel 'x' set ylabel 'y' # Axes ranges set xrange
#Ubuntu gnuplot code#
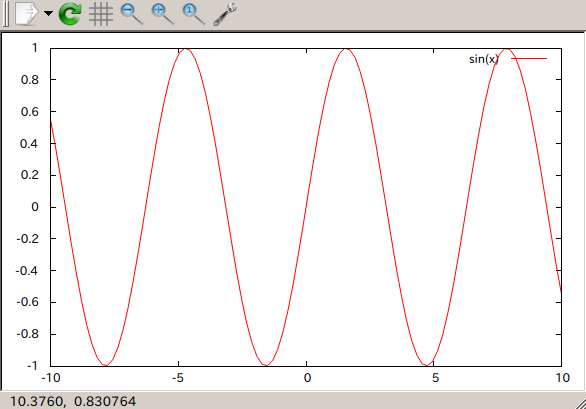
Therefore put the following code in front of the function’s definitions (in front of the plot command is sufficient, but I prefer to have the function’s definitions near the plot command). 1 Our first ugly result ( code to produce this figure)Īs you can see, we have to tune it a little bit to get a nice graph. This should produce in both cases a graph as shown in Fig. gnuplot> load 'path_to_your_file/introduction.gnu'
#Ubuntu gnuplot windows#
Under Windows you can start gnuplot with the wgnuplot.exe file and then plot the introduction file by the following command. Now we save our file as introduction.gnu and execute it by running the following command in BASH under Linux. The backslash tells gnuplot that we have a line break at this position. We want to plot more than one function that’s why we have to divide the two commands with a comma. # Plot plot f( x) title 'sin(x)' with lines linestyle 1, \ g( x) notitle with lines linestyle 2Īs you can see, the definitions of functions in gnuplot are straight forward. Therefore we specify our functions and plot them: a = 0.9 f( x) = a * sin( x) In our first graph we want to plot a sinusoid and a cosinus. For them we specified a colour, the line type where 1 is a normal line and also the line width. We use the set command and specify the border line width and two line styles with the number 1 and 2. # Line width of the axes set border linewidth 1.5 # Line styles set style line 1 linecolor rgb '#0060ad' linetype 1 linewidth 2 set style line 2 linecolor rgb '#dd181f' linetype 1 linewidth 2 Therefore we have to write this line of code: set terminal wxt size 350, 262 enhanced font 'Verdana,10' persistĪfter that we will specify the style of the output, because the default gnuplot output is ugly in many ways. The most common are png, svg, postscript or LaTeX output, but first we will start with the output just on the screen using the wxWidgets toolkit.
#Ubuntu gnuplot download#
Therefore open a text file in your preferred text editor, or directly download the code for this tutorial.įirstly we have to tell gnuplot the output terminal we want to use. In this tutorial you will create your first gnuplot figure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
